Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing Process
Stainless Steel
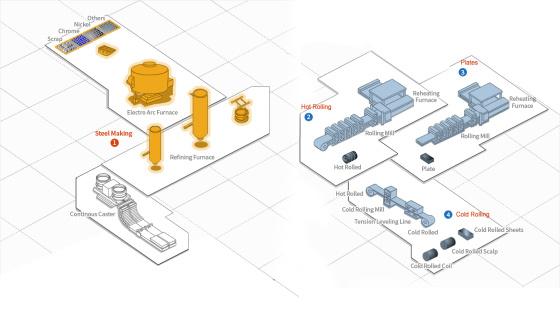
1. Steel Making: Steelmaking has the greatest impact on
the quality and cost of steel products. We has state-of-the-art AOD,
VOD and continuous casting facilities..
2. Hot Rolling: Slabs made in the steelmaking plant are
rolled into black coils of highly refined thickness and shape before
being made into white coils to the needs of customers through heat
treatment, pickling and finishing in the annealing and pickling plant.
White coils so produced are used for cold rolling, pipes and sheets.
3. Plates: Slabs produced at the steelmaking plant
undergo rolling, heat-treatment and a pickling process, which are then
cut into sizes as ordered and delivered to the customer. Thick plates
are used by the heavy chemical industries that require corrosion
resistance, such as petrochemicals, power plant facilities, paper
manufacturing and special shipbuilding.
4.Cold Rolling: JIUZHOU is equipped with 20 high
cluster mills, bright annealing line, TLL (Tension Leveling Line), AFC
(Automatic Flatness Control), AGC (Automatic Gauge Control), which
enable the production of cold rolled products of 0.1-3.0mm in thickness
and up to 1580mm in width in various shapes and surface treatment.
Hot Rolled Steel
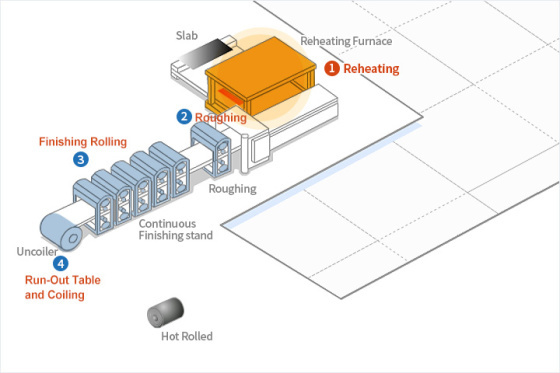
1. Reheating: Hot rolled coils pass through a pickling
line, where scale breaker machines and hydrochloric acid solutions are
used to remove any surface scale and/or oxide film that which causes
surface flaws during the final stage of cold rolled steel processing.
2. Roughing: In this process, slabs whose surface
scale share has been removed are made into rolled materials with the
proper shape, thickness, and width. In the entry and exit area of the
roughing mill, an edger rolls the strip in the width direction using an
Automatic Width Control (AWC) system.
3. Finishing Rolling: The purpose of finishing rolling
is to adjust the thickness and width of a coil to the specified
dimensions and to produce a smooth surface and shape at the desired
finishing temperature appropriate for its intended use. Our up-to-date
equipment, including Work Roll Shift Mills, Pair Cross Mills and On-line
Roll Grinders (ORG), enhances plant productivity and improves the
quality of the finished coils by controlling the crown shape.
4. Run-Out Table and Coiling: Steel strips, after the
finishing mill, are passed to the run-out table where they are coiled.
While being rolled on the table, the strips are sprayed with water to
cool them to the proper temperature for coiling.
Cold Rolled Steel
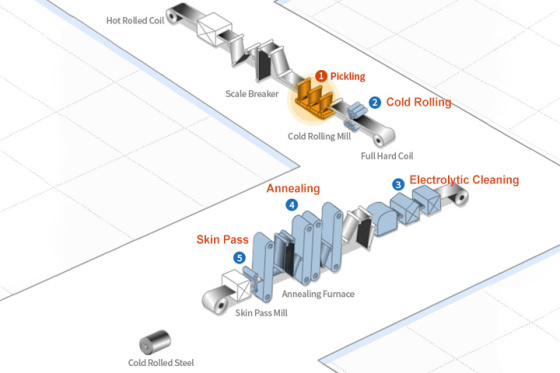
1. Pickling: Hot rolled coils pass through a pickling
line, where scale breaker machines and hydrochloric acid solutions are
used to remove any surface scale and/or oxide film that which causes
surface flaws during the final stage of cold rolled steel processing.
2. Cold Rolling: Pickled coils are cold rolled in
tandem mills to a specified thickness, typically 40 to 90%, of original
material dimensions. Fully automated shape adjustment is ensured through
state of the art process machinery.
3. Electrolytic Cleaning: The purpose of electrolytic
cleaning is to remove lubricant oil and contaminants on the cold rolled
steel prior to the annealing process.
4. Annealing: This is a highly productive manufacturing
method whereby steel products with extra deep drawing qualities and
high tensile strength can be produced. Two annealing methods are
commonly used: batch annealing and continuous annealing.
5. Skin Pass: This final rolling process is performed
in order to remove minor surface defects such as stretch marks and to
produce a smooth, lustrous surface. Skin Pass results in a further
thickness reduction of about 1%.
Galvanized Steel
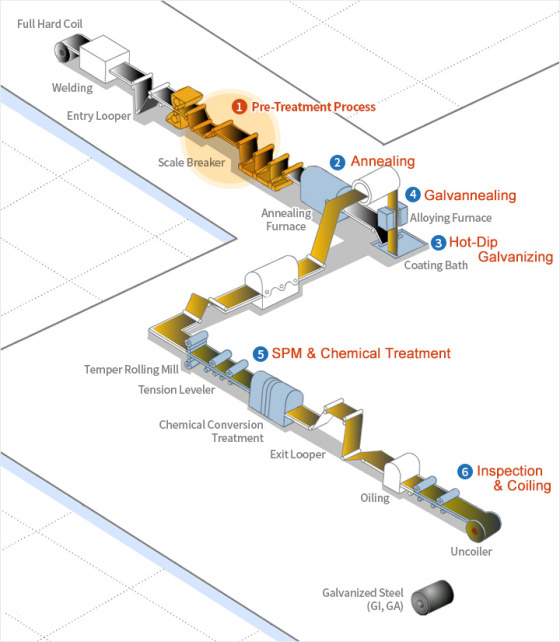
1. Pre-Treatment Process: Some rolling oil and other
contaminants remain on the surface of cold rolled steel sheets following
processing. These are removed by passing the electrically charged sheet
through an alkaline solution which induces an electrochemical reaction.
2. Annealing: The material properties of the
pre-treated steel sheet can be altered and improved through
recrystallization during the annealing process.
3. Hot-Dip Galvanizing: After passing through the
annealing furnace, steel sheets are dipped into a zinc pot where molten
Zn is coated onto the surface. The desired coating weight is achieved by
removing excess zinc before solidification with high-pressure air from
an air knife.
4. Galvannealing: The surface of a steel sheet, after
the air knife, can be coated with a zinc compound prior to reheating in
an annealing process. Zn atoms diffuse into the Fe to create a Zn-Fe
series alloy.
5. SPM & Chemical Treatment: In order to achieve a
flat surface and an elegant finish, the steel sheet is processed with a
skin pass mill. In order to prevent the white rust, which often forms on
the surface of activated zinc, and to improve corrosion resistance, the
surface is coated with a Cr-free resin.
6. lnspection & Coiling: In order to achieve a flat
surface and an elegant finish, the steel sheet is processed with a skin
pass mill. In order to prevent the white rust, which often forms on the
surface of activated zinc, and to improve corrosion resistance, the
surface is coated with a Cr-free resin.
